Have you ever had a brilliant idea for an app or program but felt completely overwhelmed about where to even begin? You’re not alone. The question “how can I develop a software?” has been the starting point for every developer, from hobbyists to the creators of global platforms like Facebook and Spotify.
The good news is that software development is a structured process, and with the right roadmap, anyone can learn to turn their idea into a functional reality. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the entire software development lifecycle, from that initial spark of an idea to launching and maintaining your application.
What is Software Development?
At its core, software development is the process of conceiving, specifying, designing, programming, documenting, testing, and bug fixing involved in creating and maintaining applications, frameworks, or other software components.
Think of it like building a house:
- Planning: You need blueprints and permits (your plan and design).
- Construction: You lay the foundation and build the structure (coding).
- Inspection: You check everything works (testing).
- Moving In: You hand over the keys (deployment).
- Maintenance: You fix leaks and make renovations (updates and bug fixes).
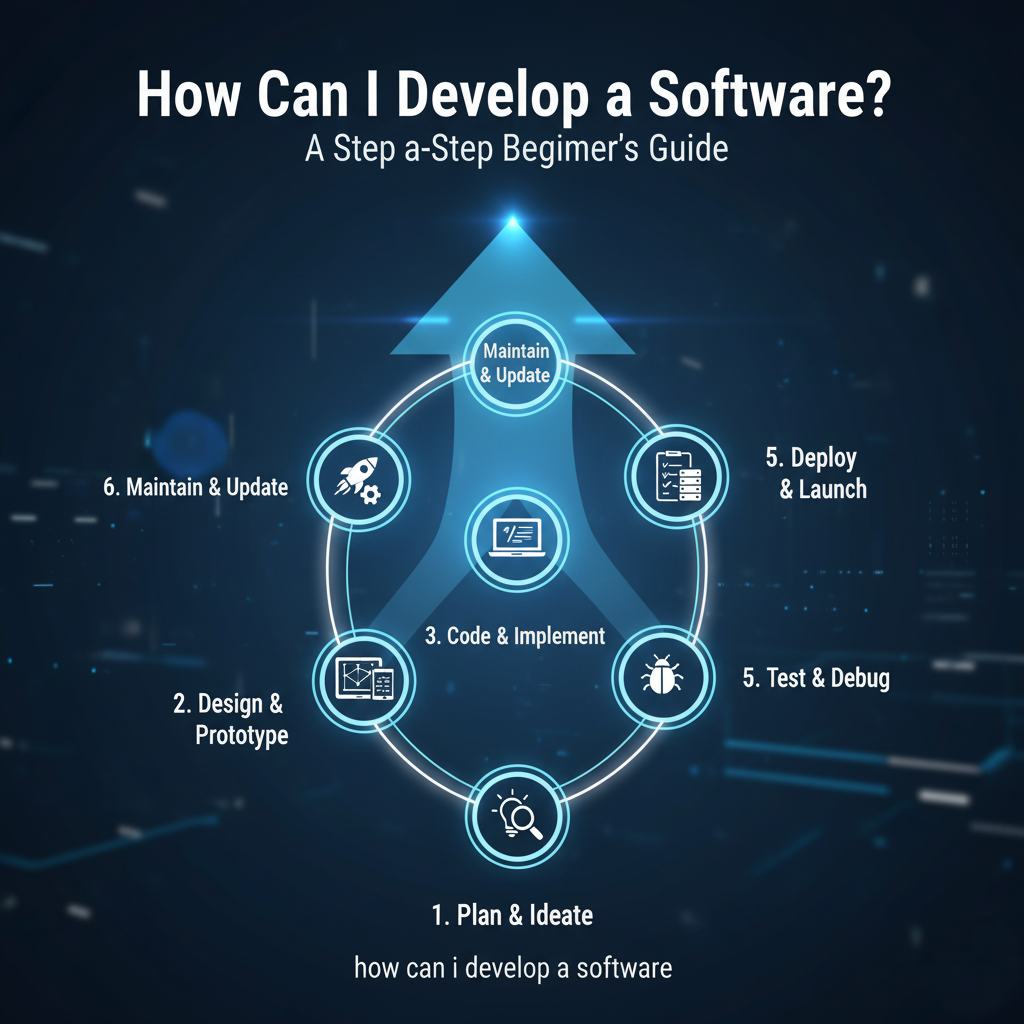
A Step-by-Step Guide to Developing Software
Step 1: Ideation and Planning (The Blueprint)
This is the most critical phase. Before writing a single line of code, you must have a clear vision.
- Define the Problem: What specific problem does your software solve? Who is it for? Be as precise as possible.
- Market Research: Are there existing solutions? What can you do better? Understanding the landscape prevents you from reinventing the wheel.
- Define Features (MVP): List all the features you want. Then, prioritize them to define your Minimum Viable Product (MVP)—the simplest version of your product that is still functional. This allows you to launch faster and get user feedback early.
- Choose Your Technology Stack: This is the set of technologies you’ll use. For beginners, simpler stacks are best.
- Frontend (what the user sees): HTML, CSS, JavaScript (React or Vue.js are popular frameworks).
- Backend (the server-side logic): Python (Django/Flask), JavaScript (Node.js), or Ruby (Ruby on Rails).
- Database: MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB.
Step 2: Design and Prototyping
Now, you design the user experience and the architecture.
- Wireframing: Create simple sketches of each screen of your application. Tools like Figma or Adobe XD are excellent for this and are free for beginners.
- Architecture Design: Plan how the different parts of your application will interact. How will data flow from the user to the database and back?
- Prototype: Turn your wireframes into a clickable model. This helps visualize the user journey and spot potential issues before development begins.
Step 3: Development (The Coding Phase)
This is where you bring the design to life.
- Set Up Your Environment: Install a code editor (Visual Studio Code is a fantastic free option) and version control software (Git is essential for tracking changes and collaborating).
- Start Coding: Break down the project into small, manageable tasks and start coding them one by one. Focus on building the core functionality of your MVP first.
- Follow Best Practices: Write clear, commented code. This will help you and others understand it later. Use version control (e.g., GitHub) to save your progress regularly.
Step 4: Testing and Quality Assurance (QA)
You must rigorously test your software to find and fix bugs.
- Unit Testing: Testing individual components or functions to ensure they work correctly on their own.
- Integration Testing: Testing how different modules work together.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Having real users (or testers) try the software to see if it meets their needs and is intuitive to use.
- Bug Fixing: This is an iterative process. Find a bug, fix it, test again.
Step 5: Deployment (Going Live)
This is the exciting part—releasing your software to the world.
- Choose a Hosting Provider: For web applications, services like AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, or Heroku are popular choices. For mobile apps, you’ll deploy to the Apple App Store and Google Play Store.
- Deploy: This involves moving your code from your local machine to a live server so users can access it. Many platforms offer continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines to automate this.
Step 6: Maintenance and Updates
Software development doesn’t end at launch. It’s an ongoing process.
- Monitor Performance: Use tools to track errors, crashes, and user behavior.
- Gather Feedback: Listen to your users. What features do they want? What bugs are they encountering?
- Release Updates: Regularly update your software to fix bugs, improve security, and add new features.
Essential Tools for Beginners
- Code Editor: Visual Studio Code (VS Code)
- Version Control: Git and GitHub
- Design & Prototyping: Figma
- Project Management: Trello or Jira
- Communication: Slack or Discord
How to Learn Software Development
The resources have never been more accessible.
- Free Online Courses: Websites like freeCodeCamp, Coursera, and edX offer excellent introductory courses.
- YouTube Tutorials: Channels like Traversy Media, The Net Ninja, and Programming with Mosh provide thousands of hours of free, high-quality content.
- Practice, Practice, Practice: The only way to learn is by doing. Start with small projects like a to-do list app or a simple calculator and gradually increase complexity.
- Join Communities: Platforms like Stack Overflow, Reddit’s r/learnprogramming, and Discord servers are invaluable for getting help and connecting with other learners.
Do You Need a Team?
For a simple app, you can absolutely learn and build it yourself. However, for more complex projects, you might need a team:
- UI/UX Designer: To create the visual design and user flow.
- Backend Developer: To handle server, database, and application logic.
- Frontend Developer: To build the user interface.
- QA Tester: To rigorously test the application.
You can find collaborators on platforms like LinkedIn or through coding communities.
Conclusion
Learning how to develop a software is a marathon, not a sprint. It requires patience, persistence, and a willingness to problem-solve. Don’t be discouraged by complex jargon or initial challenges. Every expert developer was once a beginner asking the exact same question.
Start today. Choose a small idea, pick a language, and follow the steps outlined above. Build, break, fix, and learn. Your journey to creating something amazing is just a single step away.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the easiest programming language for beginners?
A: Python is widely considered one of the easiest languages to start with due to its simple, readable syntax and versatility. JavaScript is also a great choice if you’re interested in web development.
Q: How long does it take to develop a software?
A: It depends entirely on the complexity. A simple mobile app could take a single developer a few months, while a complex enterprise application could take a large team a year or more. Starting with an MVP is key to getting something functional out quickly.
Q: Can I develop software without knowing how to code?
A: Yes, to an extent. No-code/low-code platforms like Bubble or Adalo allow you to build applications using visual interfaces. However, for full customization and complex functionality, learning to code is essential.
Q: How much does it cost to develop software?
A: If you develop it yourself, the cost can be $0 besides your time and any paid hosting/services. Hiring a freelance developer can cost from $5,000 to $50,000+ for a simple app, while a professional agency can charge $100,000+ for more complex projects.